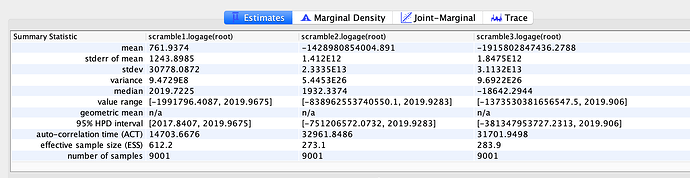
Three more high-quality full-length genomes were added to the China National GeneBank. I updated the analyses to include these new genomes and at the suggestion of Oliver Pybus, also provide an additional analysis randomizing tip dates to show that the estimates are informed more by the data than choice of priors. The main conclusions remain the same, although we now obtain significantly better mixing of the MCMC and narrower 95% HPDs. Despite this, please note that this is still work in progress and precaution should be taken interpreting the values and all estimates should be considered based on their intervals and not point values.
Data
As of January 27, 2020, 30 full-length nCoV-2019 high quality genomes are available. The final dataset contains 36 SNPs after removing 9 SNPs that are likely due to sequencing errors. Acknowledgements of the genome sequences used in this analysis are in the table at the end of this document.
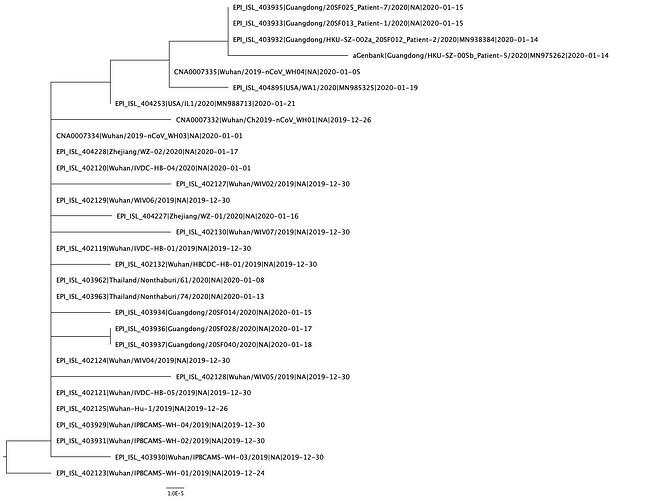
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree was created using PhyML and in agreement with previous analyses still shows limited genetic variation in the sampled viruses, which is consistent with a recent common ancestor.
The genetic data is still highly suggestive of a single-point introduction into the human population followed by sustained human-to-human transmission with no further evidence of zoonotic transmissions.
Evolutionary rate
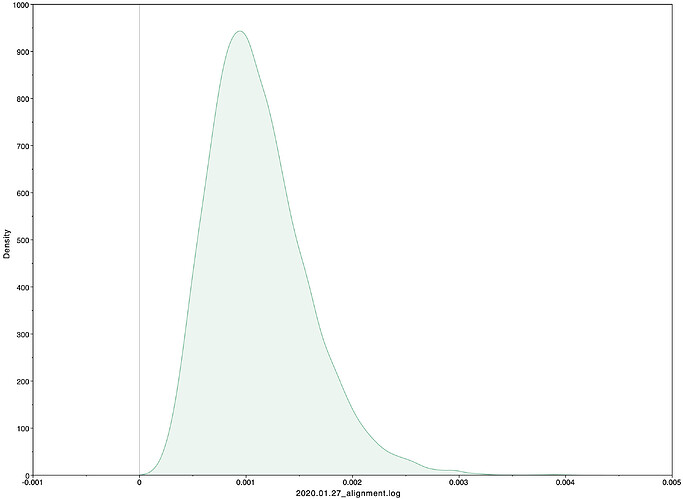
To estimate the substitution rate of nCoV-2019, I used BEAST with a simple model consisting of HKYγ, strict clock with a CTMC rate prior, and a constant tree prior. The median estimate for the substitution rate is very similar to other RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV, Ebola virus, Zika virus, and others at ~ 1E-3 subs/site/year. Compared to previous analyses, we’re now starting to see better estimates of the rate.
|Median|95% HPD
|—|—|—|—|
1.05E-3 | 3.29E-4 - 2.03E-3
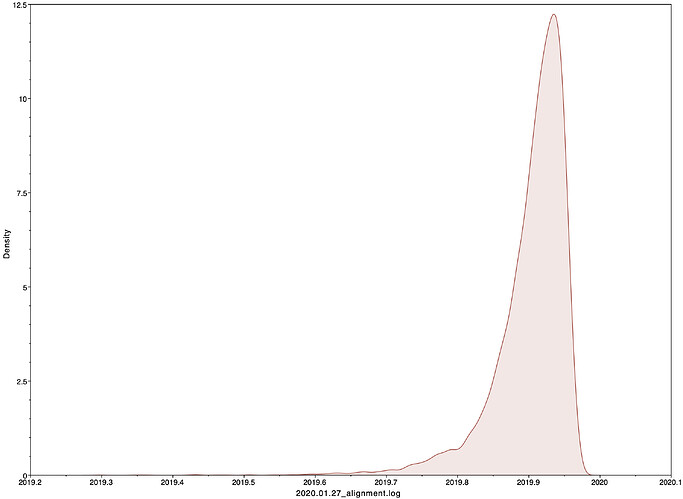
Date of the MRCA
I next estimated the date of the MRCA of the sampled nCoV-2019 genomes and the results were in agreement with previous estimates.
|Median|95% HPD
|—|—|—|—|
01 Dec 2019 | 20 Oct 2019 - 20 Dec 2019
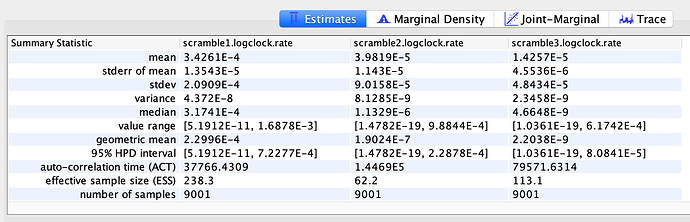
Randomization analysis
To test whether the estimates could have been strongly influenced by the priors, three independent alignments shuffling tip dates were created and analyzed with BEAST using the same model as described above. In all cases did these analyses fail to capture meaningful rate and date estimates, suggesting that the estimates above are primarily informed by the data and not choice of priors. Despite this, all caveats described above still hold true and the dataset is still limited by size and sampling may be biased. This means that the addition of more sequencing data could likely change these estimates.
Note: ideally these analyses should be done 100+ times and include ‘leave-one-out’ analyses. I will try to do those at a later date.
Rate (three randomized alignments)
TMRCA (three randomized alignments)
Log files can be downloaded here. Please contact me directly for XMLs and alignments.
Acknowledgements and Genome Availability
| Strain | Authors | Source | Lab |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPI_ISL_402119 | Wenjie Tan, et al. | GISAID | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC |
| EPI_ISL_402120 | Wenjie Tan, et al. | GISAID | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC |
| EPI_ISL_402121 | Wenjie Tan, et al. | GISAID | National Institute for Viral Disease Control and Prevention, China CDC |
| EPI_ISL_402123 | Lili Ren, et al. | GISAID | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| EPI_ISL_402124 | Peng Zhou, et al. | GISAID | Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| EPI_ISL_402125 | Zhang, et al. | GISAID | National Institute for Communicable Disease Control and Prevention (ICDC) Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention (China CDC) |
| EPI_ISL_402127 | Peng Zhou, et al. | GISAID | Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| EPI_ISL_402128 | Peng Zhou, et al. | GISAID | Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| EPI_ISL_402129 | Peng Zhou, et al. | GISAID | Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| EPI_ISL_402130 | Peng Zhou, et al. | GISAID | Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| EPI_ISL_402132 | Bin Fang, et al. | GISAID | Hubei Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403929 | Lili Ren, et al. | GISAID | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| EPI_ISL_403930 | Lili Ren, et al. | GISAID | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| EPI_ISL_403931 | Lili Ren, et al. | GISAID | Institute of Pathogen Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College |
| EPI_ISL_403932 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403933 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403934 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403935 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403936 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403937 | Min Kang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Guangdong Provincial Center for Diseases Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_403962 | Pilailuk, et al. | GISAID | Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand |
| EPI_ISL_403963 | Pilailuk, et al. | GISAID | Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand |
| EPI_ISL_404227 | Yin Chen, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_404228 | Yanjun Zhang, et al. | GISAID | Department of Microbiology, Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| EPI_ISL_404253 | Ying Tao, et al. | GISAID | IL Department of Public Health Chicago Laboratory |
| EPI_ISL_404895 | Queen, et al. | GISAID | Division of Viral Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| MN975262 | Chan et al. | Genbank | State Key Laboratory of Emerging Infectious Diseases |
| CNA0007332 | Chen et al. | China National GeneBank | BGI |
| CNA0007334 | Chen et al. | China National GeneBank | BGI |
| CNA0007335 | Chen et al. | China National GeneBank | BGI |