PSET results updated with new 2019-nCoV genomes; 655 total genomes. Just using the subset of genomes on GISAID marked as high quality sampled from humans. Sequence IDs tested in this analysis listed here: 655_ids.zip (1.4 KB)
Previous Noblis assays showed some false negatives due to Ns, sequence gaps, and in one case the assay’s position at the very start of the genome. These have been replaced with five new assays generated at a later date using 96 complete genomes. The Noblis.57 assay and the German ncov_e_gene assay each have one FN that’s due to a stretch of Ns. All other assays still performing very well in silico against new sequences.
Table 1. Results from PSET analysis. The five Noblis assays were compared alongside the four assays from Corman and three assays from the CDC. Each assay was tested using 2019-nCoV (655 genomes) as the intended target. All off-target hits (TN, PF, FP) are to entries in NCBI BLAST databases (nt, gss, and env_nt).
| identifier | provider | PT | TP | TN | PF | FP | FN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noblis.12 | Noblis | 653 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Noblis.40 | Noblis | 635 | 20 | 316 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Noblis.42 | Noblis | 655 | 0 | 275 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Noblis.44 | Noblis | 655 | 0 | 277 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Noblis.57 | Noblis | 654 | 0 | 359 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| ncov_e_gene | Corman et al | 651 | 3 | 42 | 353 | 15 | 1 |
| ncov_n_gene | Corman et al | 652 | 3 | 55 | 0 | 339 | 0 |
| ncov_rdrp_1 | Corman et al | 0 | 655 | 75 | 433 | 87 | 0 |
| ncov_rdrp_2 | Corman et al | 1 | 654 | 526 | 1 | 66 | 0 |
| cdc_n1 | CDC | 647 | 8 | 363 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| cdc_n2 | CDC | 653 | 2 | 361 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| cdc_n3 | CDC | 628 | 27 | 17 | 0 | 346 | 0 |
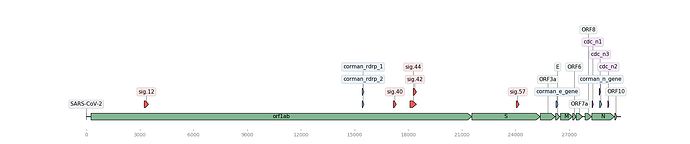
Figure 1. Map of the SARS-CoV-2 genome (NCBI Accession: MN908947.3) with assay signature locations (created using DNA Features Viewer Python library). Noblis assays in red, Corman assays in blue, CDC assays in purple, and gene regions in green.